Economy chaina
Since the late 1970s China has moved from a closed, centrally planned system to a more market-oriented one that plays a major global role - in 2010 China became the world's largest exporter. Reforms began with the phasing out of collectivized agriculture, and expanded to include the gradual liberalization of prices, fiscal decentralization, increased autonomy for state enterprises, creation of a diversified banking system, development of stock markets, rapid growth of the private sector, and opening to foreign trade and investment. China has implemented reforms in a gradualist fashion. In recent years, China has renewed its support for state-owned enterprises in sectors it considers important to "economic security," explicitly looking to foster globally competitive national champions. After keeping its currency tightly linked to the US dollar for years, in July 2005 China revalued its currency by 2.1% against the US dollar and moved to an exchange rate system that references a basket of currencies. From mid 2005 to late 2008 cumulative appreciation of the renminbi against the US dollar was more than 20%, but the exchange rate remained virtually pegged to the dollar from the onset of the global financial crisis until June 2010, when Beijing allowed resumption of a gradual appreciation. The restructuring of the economy and resulting efficiency gains have contributed to a more than tenfold increase in GDP since 1978. Measured on a purchasing power parity (PPP) basis that adjusts for price differences, China in 2010 stood as the second-largest economy in the world after the US, having surpassed Japan in 2001. The dollar values of China's agricultural and industrial output each exceed those of the US; China is second to the US in the value of services it produces. Still, per capita income is below the world average. The Chinese government faces numerous economic challenges, including: (a) reducing its high domestic savings rate and correspondingly low domestic demand; (b) sustaining adequate job growth for tens of millions of migrants and new entrants to the work force; (c) reducing corruption and other economic crimes; and (d) containing environmental damage and social strife related to the economy's rapid transformation. Economic development has progressed further in coastal provinces than in the interior, and by 2011 more than 250 million migrant workers and their dependents had relocated to urban areas to find work. One consequence of population control policy is that China is now one of the most rapidly aging countries in the world. Deterioration in the environment - notably air pollution, soil erosion, and the steady fall of the water table, especially in the North - is another long-term problem. China continues to lose arable land because of erosion and economic development. The Chinese government is seeking to add energy production capacity from sources other than coal and oil, focusing on nuclear and alternative energy development. In 2010-11, China faced high inflation resulting largely from its credit-fueled stimulus program. Some tightening measures appear to have controlled inflation, but GDP growth consequently slowed to near 9% for 2011. An economic slowdown in Europe is expected to further drag Chinese growth in 2012. Debt overhang from the stimulus program, particularly among local governments, and a property price bubble challenge policy makers currently. The government's 12th Five-Year Plan, adopted in March 2011, emphasizes continued economic reforms and the need to increase domestic consumption in order to make the economy less dependent on exports in the future. However, China has made only marginal progress toward these rebalancing goals.
GDP (purchasing power parity)
$11.29 trillion (2011 est.)
$10.34 trillion (2010 est.)
$9.356 trillion (2009 est.)
note: data are in 2011 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate)

$6.989 trillion
note: because China's exchange rate is determine by fiat, rather than by market forces, the official exchange rate measure of GDP is not an accurate measure of China's output; GDP at the official exchange rate substantially understates the actual level of China's output vis-a-vis the rest of the world; in China's situation, GDP at purchasing power parity provides the best measure for comparing output across countries (2011 est.)
GDP - real growth rate
9.2% (2011)
10.5% (2010)
9.2% (2009)
GDP - per capita (PPP)
$8,400 (2011 est.)
$7,500 (2010 est.)
$7,000 (2009 est.)
note: data are in 2011 US dollars
GDP - composition by sector
agriculture: 10.1%
industry: 46.8%
services: 43.1% (2011 est.)
Population below poverty line
13.4%
note: in 2011, China set a new poverty line at RMB 2300 (approximately US $363; this new standard is significantly higher than the line set in 2009, and as a result, 128 million Chinese are now considered below the poverty line (2011)
Labor force
795.5 million
note: by the end of 2011, population at working age (15-64 years) was 1.0024 billion (2011 est.)
Labor force - by occupation
agriculture: 36.7%
industry: 28.7%
services: 34.6% (2008 est.)
Unemployment rate
6.5% (2011 est.)
6.1% (2010 est.)
note: registered urban unemployment, which excludes private enterprises and migrants was 4.1% in 2010
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.5%
highest 10%: 15%
note: data are for urban households only (2008)
Distribution of family income - Gini index

48 (2009)
41.5 (2007)
Investment (gross fixed)
54.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget
revenues: $1.646 trillion
expenditures: $1.729 trillion (2011 est.)
Taxes and other revenues
23.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-)
-1.2% of GDP (2011 est.)
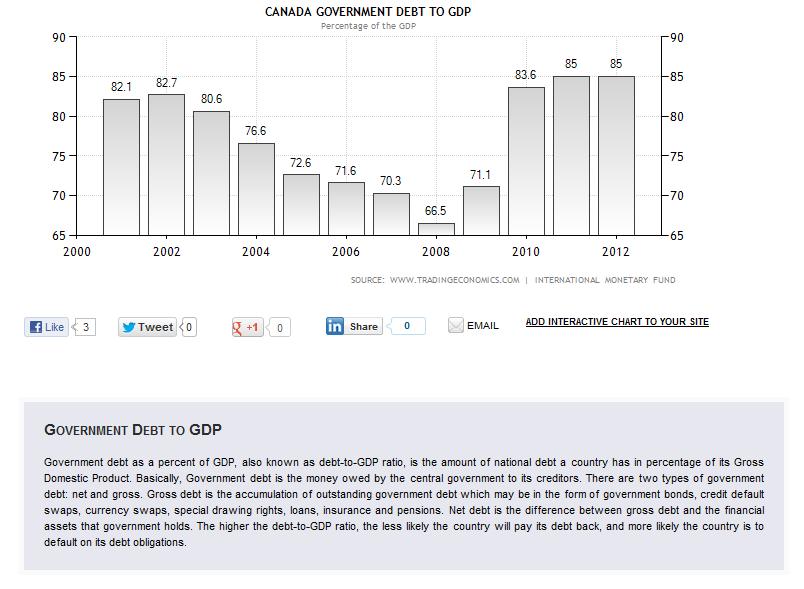
Public debt
43.5% of GDP (2011)43.5% of GDP (2010)
note: official data; data cover both central government debt and local government debt, which China's National Audit Office estimated at RMB 10.72 trillion (approximately US$1.66 trillion)in 2011; data exclude policy bank bonds, Ministry of Railway debt, China Asset Management Company debt, and non-performing loans
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.4% (2011 est.)
3.3% (2010 est.)
Central bank discount rate
2.25% (31 December 2010 est.)
3.25% (31 December 2010 est.)
Commercial bank prime lending rate
6.56% (31 December 2011 est.)
5.81% (31 December 2010 est.)
Stock of money
$2.434 trillion (31 December 2008)
$2.09 trillion (31 December 2007)
Stock of narrow money
$4.599 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
$4.046 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
Stock of broad money
$13.52 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
$11.01 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
Stock of quasi money
$4.523 trillion (31 December 2008)
$3.437 trillion (31 December 2007)
Stock of domestic credit
$10.72 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
$8.868 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares
$3.408 trillion (30 December 2011 est.)
$4.028 trillion (31 December 2010)
$5.008 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
Agriculture - products
world leader in gross value of agricultural output; rice, wheat, potatoes, corn, peanuts, tea, millet, barley, apples, cotton, oilseed; pork; fish

Industries
world leader in gross value of industrial output; mining and ore processing, iron, steel, aluminum, and other metals, coal; machine building; armaments; textiles and apparel; petroleum; cement; chemicals; fertilizers; consumer products, including footwear, toys, and electronics; food processing; transportation equipment, including automobiles, rail cars and locomotives, ships, and aircraft; telecommunications equipment, commercial space launch vehicles, satellites
Industrial production growth rate
13.9% (2011 est.)
Electricity - production
4.604 trillion kWh (2011)
Electricity - production by source
fossil fuel: 80.2%
hydro: 18.5%
nuclear: 1.2%
other: 0.1% (2001)
Electricity - consumption
4.693 trillion kWh (2011)
Electricity - exports
19.06 billion kWh (2010)
Electricity - imports
55.45 billion kWh (2010)
Oil - production
4.073 million bbl/day (2011)
Oil - consumption
9.4 million bbl/day (2011 est.)

Oil - exports
506,500 bbl/day (2011 est.)

Oil - imports
5.08 million bbl/day (2011 est.)

Oil - proved reserves
14.8 billion bbl (1 January 2011 est.)
Natural gas - production
102.5 billion cu m (2011)
Natural gas - consumption
129 billion cu m (2011 est.)
Natural gas - exports
3.21 billion cu m (2011 est.)
Natural gas - imports
30 billion cu m (2011 est.)
Natural gas - proved reserves
800 billion cu m (1 January 2011 est.)
Current Account Balance
$280.6 billion (2011 est.)
$305.4 billion (2010 est.)
Exports
$1.898 trillion (2011 est.)
$1.578 trillion (2010 est.)
Exports - commodities
electrical and other machinery, including data processing equipment, apparel, textiles, iron and steel, optical and medical equipment
Exports - partners
US 17.7%, Hong Kong 14.1%, Japan 7.8%, South Korea 4.4%, Germany 4% (2009)
Imports
$1.743 trillion (2011 est.)
$1.327 trillion (2010 est.)
Imports - commodities
electrical and other machinery, oil and mineral fuels, optical and medical equipment, metal ores, plastics, organic chemicals
Imports - partners
Japan 11.2%, South Korea 9.3%, US 7%, Germany 5.3%, Australia 4.7% (2009)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.236 trillion (31 December 2011 est.)
$2.895 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
Debt - external
$697.2 billion (30 September 2011 est.)
$548.9 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment - at home
$776 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
$578.8 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad
$322 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
$317.2 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
Exchange rates
Renminbi yuan (RMB) per US dollar -
6.4614 (2011 est.)
6.7695 (2010 est.)
6.8314 (2009)
6.9385 (2008)
7.61 (2007)